Stuart Russell:目前的人工智能系统没有通用性,因为电路无法很好地捕捉通用性。我们已经在大型语言模型很难学习算术的基本规则中看到了这一点。尽管有数百万个例子,之前击败人类的人工智能围棋系统还是无法正确理解 “大龙” 和 “死活” 的概念,作为业余围棋选手的研究员开发出了一套策略,战胜了围棋程序(“20230223 绝艺”)。
《Sparks of Artificial General Intelligence: Early experiments with GPT-4》
8.2 Lack of planning in arithmetic/reasoning problems
GPT-4:7 * 4 + 8 * 8 = 88
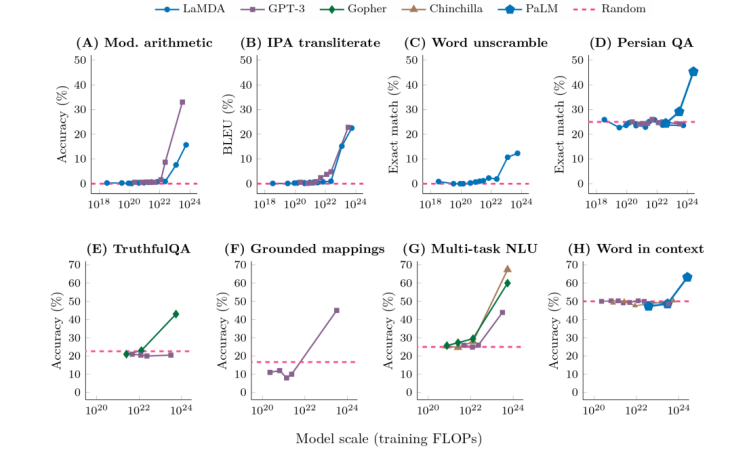
作者用 100 个随机样本对模型进行了测试,在 0 到 9 之间均匀生成四个数字,得到的准确率只有 58%。这只涉及到个位数的乘法和两位数字的加法,一个具备基本数学知识的小学生就能解决这个问题,当数字在 10 ~ 19 之间和 20 ~ 39 之间均匀选择时,准确度分别下降到 16% 和 12%,当数字在 99 和 199 之间时,准确度下降到零。
《哥德尔、埃舍尔、巴赫:集异璧之大成 Gödel, Escher, Bach: An Eternal Golden Braid》Hofstadter
CHAPTER XIX Artificial Intelligence: Prospects
Ten Questions and Speculations
Question: Will a thinking computer be able to add fast?(智能计算机是否能更快地做加法?)
Speculation: Perhaps not. We ourselves are composed of hardware which does fancy calculations but that doesn’t mean that our symbol level, where “we” are, knows how to carry out the same fancy calculations. Let me put it this way: there’s no way that you can load numbers into your own neurons to add up your grocery bill. Luckily for you, your symbol level (i.e., you) can’t gain access to the neurons which are doing your thinking-otherwise you’d get addle-brained. To paraphrase Descartes again:
“I think; therefore I have no access to the level where I sum.” (我思,故我无法进入我算的层次)
Why should it not be the same for an intelligent program? It mustn’t be allowed to gain access to the circuits which are doing its thinking otherwise it’ll get addle-CPU’d. Quite seriously, a machine that can pass the Turing test may well add as slowly as you or I do, and for similar reasons. It will represent the number 2 not just by the two bits “10”, but as a full-fledged concept the way we do, replete with associations such as its homonyms “too” and “to”, the words “couple” and “deuce”, a host of mental images such as dots on dominos, the shape of the numeral ‘2’, the notions of alternation, evenness,
oddness, and on and on … With all this “extra baggage” to carry around, an intelligent program will become quite slothful in its adding. Of course, we could give it a ‘ pocket calculator , so to speak (or build one in). Then it could answer very fast, but its performance would be just like that of a person with a pocket calculator. There would be two separate parts to the machine: a reliable but mindless part and an intelligent but fallible part. You couldn’t rely on the composite system to be reliable, any more than a composite of person and machine is necessarily reliable. So if it’s right answers you’re after, better stick to the pocket calculator alone-don’t throw in the intelligence!
扩展一下:泛化能力/鲁棒性与出错/幻觉/胡话、原理黑箱是通用智能的一体两面(2.2.1.1.3 容错、自修复、鲁棒性)。
有些场景中,大模型的一些现有缺陷对商用的影响没那么大,甚至可能是助益。如强调个性化和趣味性的聊天应用 character.ai 创始人说:“我并不认为幻觉是需要解决的问题,我甚至很喜欢它,这是模型有趣的特点。” 在 character.ai 做的 “角色扮演” 聊天场景中,幻觉是想象力的源泉。但对另一些容错很低的行业,如医疗诊断、自动驾驶、工业自动化,幻觉却危害显著。
群集模型系统:在凯文·凯利《失控:机器、社会与经济的新生物学》一书中描述了复杂系统的进化、涌现和失控。人类大脑的神经网络、蚁群、蜂群这类系统的动作是从一大堆乱哄哄却又彼此关联的事件中产生的。从群体中涌现出来的不是一系列个体行为,而是众多个体协同完成的整体动作。AI 大模型也符合群集系统的特点。由于缺乏中心控制,群集系统效率相对低,如大模型就存在信息冗余,且不可预测、不可知、不可控。但缺乏中心控制也带来了可适应、可进化、无限性和新颖性的优势,因此大模型能通过涌现自学新技能。
 词空间向量的轨迹
词空间向量的轨迹

